Understanding Kidney Stones and Treatment Options
Misconceptions and Fears
Many individuals harbor a fear of kidney stones, often associating them solely with surgery. However, amidst a cacophony of remedies ranging from herbal concoctions to surgical interventions, the need for clarity regarding treatment options emerges. Therefore, let’s unravel who requires treatment and how doctors determine the appropriate course of action. In this endeavor, I aim to demystify complex medical jargon for your understanding.
Formation of Kidney Stones and Common Mistakes
Understanding the genesis of kidney stones is paramount to exploring treatment avenues. Firstly, various misconceptions and lifestyle choices contribute to their formation. Secondly, Rigid-Scopy emerges as a method to remove stones lodged near the ureter’s end, presenting a potential solution.
Hydration
Ensuring adequate hydration is crucial, as drinking a minimum of three liters of water per day can help balance fluid levels and reduce the risk of stone formation.
Considerations for Children
Kidney stones can also affect children, often due to poor dietary habits. Encouraging a healthy lifestyle with plenty of water intake and physical activity can help prevent stone formation, especially in regions with hot climates and high consumption of processed foods.
The Role of Kidneys: Anatomy and Function
For many, the kidneys remain enigmatic organs, their vital functions often overlooked. However, clarifying the structure and significance of kidneys becomes essential. Situated beneath the rib cage, kidneys play a pivotal role in toxin removal and fluid balance. They also regulate blood pressure and produce essential compounds like active Vitamin D.
Anatomy of Kidneys
The kidneys, nestled on either side of the spine, resemble bean-shaped structures. Moreover, positioned adjacent to major blood vessels like the Aorta and inferior Vena Cava, they receive a continuous blood supply crucial for their functions.
Functions of Kidneys
Beyond toxin removal, kidneys facilitate urine production by filtering waste and excess substances from the bloodstream. Additionally, they play a pivotal role in maintaining fluid balance, regulating blood pressure, and fostering bone health through Vitamin D synthesis.
Nephrons: The Functional Units
Millions of nephrons within the kidneys orchestrate urine production by filtering blood. Comprising intricate structures like Glomeruli and epithelial cells, nephrons serve as efficient purification units. Despite filtering vast quantities of fluid, kidneys reabsorb most of it, ensuring optimal bodily function.
Formation of Kidney Stones
An interplay of fluids, minerals, and dietary habits sets the stage for kidney stone formation. Genetic predispositions or dietary excesses, particularly salt and sodium intake, exacerbate the risk. Adequate hydration emerges as a crucial preventive measure, counteracting the tendency for stone formation.
Types of Kidneys Stones
Diverse compositions characterize kidney stones, each demanding nuanced treatment approaches. Predominant varieties include Calcium Oxalate Crystals, Struvite Stones, Uric Acid Stones, and Cystine Stones. While origins vary, treatment modalities often overlap.
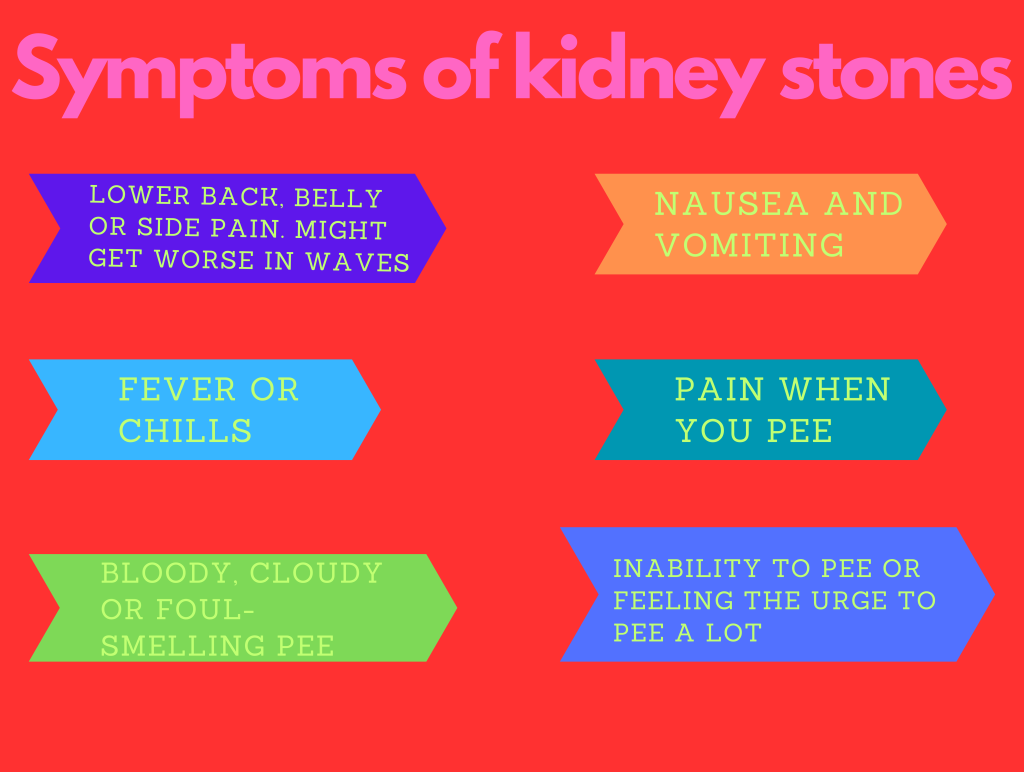
Identifying Kidney Stones
Recognition of kidney stone symptoms aids timely intervention. Pain radiating from the loin to the groin, accompanied by discomfort during urination or blood-tinged urine, signals potential stone presence. Urine color variations, from dark yellow to smoky or cloudy, offer additional diagnostic clues.
Treatment for Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can be managed through various treatment modalities depending on factors such as the number, size, and location of the stones, as well as the presence of symptoms.
Modality of Treatment
The choice of treatment modality depends on factors such as the number and size of stones, their location, and the presence of symptoms.
Number of Stones, Size, and Location
The treatment approach is influenced by the number and size of stones, as well as their location within the urinary tract.
Symptoms
Symptoms such as severe pain, blockage of urinary flow, and impaired kidney function may indicate the need for intervention.
Medications and Surgical Options
Medications may be prescribed to facilitate the breakdown and passage of stones. However, surgical, or minimally invasive options may be recommended if symptoms persist despite medication, or if there are complications such as blockage of urinary flow or intolerable pain.
Three Treatment Methods
Three common treatment methods for kidney stones include Shock Wave Lithotripsy, Ureteroscopy, and Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy.
Shock Wave Lithotripsy (SWL)
SWL involves the use of shock waves to break large kidney stones into smaller fragments that can be passed through urine. This procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis and allows for a quick recovery, although blood-stained urine may occur as a minor side effect. However, SWL may not effectively break down very large or hard stones.
Ureteroscopy
Ureteroscopy involves the insertion of a scope through the ureter to locate and remove stones. Laser technology may be used to break down stones, and a stent may be temporarily placed to alleviate urinary blockage. Ureteroscopy is minimally invasive and typically allows for a swift recovery with minimal side effects.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
PCNL is recommended for large, hard-to-break stones. It involves making a small incision near the kidney to access and remove stones. This procedure may require hospitalization and a longer recovery period compared to other methods, with regular follow-up visits to monitor progress.
Conclusion
Navigating the realm of kidney stones necessitates dispelling misconceptions and embracing informed decision-making. By elucidating their formation, functions, and treatment avenues, we empower individuals to confront this medical challenge with confidence and clarity.
