Introduction:
“Struggling with heartburn? Find comprehensive solutions here! Explore causes, symptoms, and effective treatments for this widespread digestive discomfort. Discover expert advice on managing and preventing heartburn with practical lifestyle changes, dietary tips, and trusted remedies. Heartburn, often misunderstood as a heart-related problem, results from stomach acid regurgitating into the esophagus. Our guide empowers you to understand the mechanisms behind heartburn, from lower esophageal sphincter dysfunction to trigger foods and lifestyle factors.
Learn how to identify and address risk factors such as obesity, diet choices, etc. Uncover diagnostic methods to determine the best course of action, including clinical evaluation, endoscopy, and pH monitoring. Take control of your heartburn with a range of treatment options, from over-the-counter antacids to prescription medications and even surgical interventions in severe cases. Don’t let heartburn disrupt your life. Start your journey to relief and lasting comfort today. Trust our expert guidance to help you reclaim your digestive health!”
Heartburn is characterized by a burning sensation or discomfort in the chest, often accompanied by a sour or acidic taste in the mouth. While it’s called “heartburn,” it has nothing to do with the heart itself. Instead, heartburn is primarily a gastrointestinal issue related to the stomach and esophagus. It can range from occasional mild discomfort to chronic and severe episodes that significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding the causes, mechanisms, and effective treatments for heartburn is essential for managing this condition and preventing its recurrence. In this overview, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for heartburn to provide a comprehensive understanding of this prevalent issue.

Acidity:
The one feeling that makes us experience the burn inside our stomach is acidity. There is a reason behind calling it acidity.
Causes:
⦁ Junk foods
⦁ Late night dinners
⦁ Beverages
⦁ Medicine
⦁ Alcohol symptoms
⦁ Citrus fruits.
Symptoms:
⦁ Bloating
⦁ Bloody vomiting
⦁ Weight loss for no particular reason
⦁ Burping
⦁ Nausea
⦁ Hiccups that don’t let up.
Foods to eat:
⦁ Eggs
⦁ Vegetables
⦁ Soybeans
⦁ Whole grains
⦁ Herbal teas
⦁ Raw honey
⦁ Yogurt.
Foods to avoid:
⦁ High-protein foods
⦁ Meats and processed meats
⦁ Certain dairy
⦁ Sodas
⦁ Fish


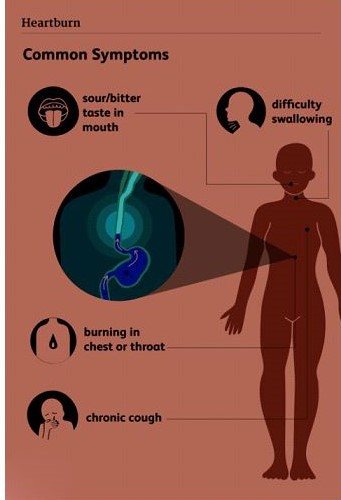
Heartburn is characterized by a burning sensation in the chest and throat, often accompanied by a sour or bitter taste in the mouth. This discomfort is caused by stomach acid refluxing into the esophagus, leading to irritation and inflammation of the esophageal lining.

Causes of Heartburn:


Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD):

GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter, the muscle that separates the esophagus from the stomach, does not function properly. This allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, leading to heartburn symptoms.

Lifestyle factors:
Several lifestyle factors can contribute to the development of heartburn:

Connective tissue disorders (i.e.Scleroderma)
Poor dietary choices, such as consuming spicy or fatty foods, can increase the likelihood of experiencing heartburn. Additionally, obesity and smoking have been linked to an increased risk of developing this condition.

Lying on the right side = More Reflux
Lying on the left side = Less Reflux.
For know more details, PLS CLICK HERE
Medications:

If you suspect that your medication is causing heartburn, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider.
Pregnancy:
Heartburn is a common complaint among pregnant women, particularly during the later stages of pregnancy. Hormonal changes and the growing fetus can put pressure on the stomach, leading to acid reflux and heartburn.

Mechanism of Heartburn:

Understanding the mechanism behind heartburn can help individuals better manage and prevent its occurrence.
Lower esophageal sphincter dysfunction:

When the lower esophageal sphincter does not close properly, stomach acid can flow back into the esophagus, causing heartburn. This dysfunction may be due to various factors, including relaxation of the sphincter muscle or increased pressure within the stomach.
Stomach acid reflux into the esophagus:

Stomach acid plays a vital role in the digestion process but can become problematic if it flows back into the esophagus. The acidic nature of stomach acid can irritate the sensitive lining of the esophagus, leading to the burning sensation characteristic of heartburn.
Irritation of the esophageal lining:

Repeated exposure to stomach acid can irritate and inflame the esophageal lining, causing further discomfort and potentially leading to complications if left untreated.
Risk Factors:
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing heartburn. These include:
Age:
As individuals age, the muscles that support the lower esophageal sphincter may weaken, making them more susceptible to heartburn.
Obesity:
Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach and lead to the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, resulting in heartburn.
Diet:

Consuming a diet high in fatty or spicy foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, and chocolate can aggravate heartburn symptoms. It is important to be mindful of these trigger foods to minimize discomfort.
Hiatal hernia:
A bulging of the top of the stomach into the diaphragm. This condition can increase the risk of experiencing heartburn.
Diagnosis:
If you suspect that you are experiencing heartburn, it is important to seek a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional. Common diagnostic methods include:
Clinical evaluation:
The healthcare provider will likely perform a physical examination to assess your overall health.
Endoscopy:
In some cases, an endoscopy may be performed to visually inspect the esophagus and stomach for signs of inflammation or other abnormalities.
pH monitoring:
pH monitoring involves the insertion of a thin tube through the nose and into the esophagus to measure the frequency and duration of acid reflux episodes over 24 hours.
Treatment:
Managing heartburn typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, over-the-counter remedies, and, in severe cases, prescription medications or surgery.
Lifestyle modifications:
Simple changes to your lifestyle can significantly reduce heartburn symptoms. Eating smaller, more frequent meals, avoiding trigger foods, maintaining a healthy weight, and refraining from smoking can all help alleviate discomfort.
Over-the-counter antacids:
Antacids work by neutralizing stomach acid and providing temporary relief from heartburn symptoms. They can be purchased over the counter and are available in various forms, such as tablets, liquids, or chewing gum.
Prescription medications:
If lifestyle modifications and over-the-counter remedies are ineffective, your healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications to reduce acid production or improve the function of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Surgery (in severe cases):
In rare cases where medication and lifestyle changes are not sufficient, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgical procedures aim to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter or repair a hiatal hernia to prevent acid reflux.
Prevention:
Preventing heartburn from occurring is key to long-term relief. Consider these preventive measures:
Dietary changes:
Avoiding trigger foods, such as spicy or acidic foods, can help prevent heartburn. Opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins instead.
Weight management:

Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate pressure on the stomach and reduce the risk of heartburn.
Avoiding trigger foods:

Identify the foods that trigger your heartburn symptoms and avoid them whenever possible.
Elevating the head of the bed
Conclusion:
Heartburn is a common and uncomfortable condition that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Understanding the causes, mechanisms, and risk factors of heartburn can empower individuals to make necessary lifestyle changes and seek appropriate treatment when needed. By focusing on prevention and adopting healthy habits, long-term relief from heartburn symptoms is achievable.